Windows (binary)
This page explains how to install ROS 2 on Windows from a pre-built binary package.
Note
The pre-built binary does not include all ROS 2 packages. All packages in the ROS base variant are included, and only a subset of packages in the ROS desktop variant are included. The exact list of packages are described by the repositories listed in this ros2.repos file.
System requirements
Only Windows 10 is supported.
Installing prerequisites
Install Chocolatey
Chocolatey is a package manager for Windows, install it by following their installation instructions:
https://chocolatey.org/install
You’ll use Chocolatey to install some other developer tools.
Install Python
Open a Command Prompt and type the following to install Python via Chocolatey:
choco install -y python --version 3.8.3
Note
Chocolatey will install Python in C:\Python38, and the rest of the installation expects it to be there.
If you’ve installed Python somewhere else, you must copy or link it to that location.
Install Visual C++ Redistributables
Open a Command Prompt and type the following to install them via Chocolatey:
choco install -y vcredist2013 vcredist140
Install OpenSSL
Open a Command Prompt and type the following to install OpenSSL via Chocolatey:
choco install -y openssl --version 1.1.1.2100
This command sets an environment variable that persists over sessions:
setx /m OPENSSL_CONF "C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin\openssl.cfg"
You will need to append the OpenSSL-Win64 bin folder to your PATH. You can do this by clicking the Windows icon, typing “Environment Variables”, then clicking on “Edit the system environment variables”. In the resulting dialog, click “Environment Variables”, then click “Path” on the bottom pane, finally click “Edit” and add the path below.
C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\bin\
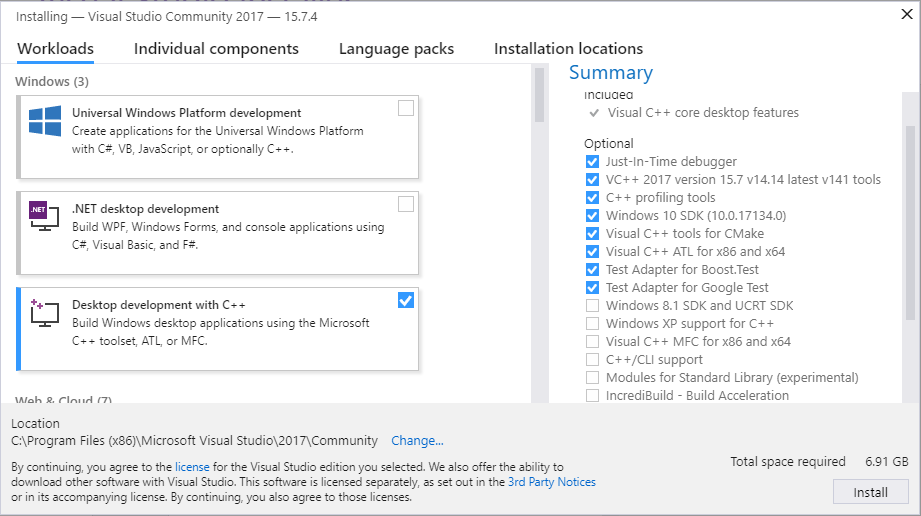
Install Visual Studio
Install Visual Studio 2019.
If you already have a paid version of Visual Studio 2019 (Professional, Enterprise), skip this step.
Microsoft provides a free of charge version of Visual Studio 2019, named Community, which can be used to build applications that use ROS 2. You can download the installer directly through this link.
Make sure that the Visual C++ features are installed.
An easy way to make sure they’re installed is to select the Desktop development with C++ workflow during the install.
Make sure that no C++ CMake tools are installed by unselecting them in the list of components to be installed.
Install OpenCV
Some of the examples require OpenCV to be installed.
You can download a precompiled version of OpenCV 3.4.6 from here.
Assuming you unpacked it to C:\opencv, type the following on a Command Prompt (requires Admin privileges):
setx /m OpenCV_DIR C:\opencv
Since you are using a precompiled ROS version, we have to tell it where to find the OpenCV libraries.
You have to extend the PATH variable to C:\opencv\x64\vc16\bin.
Install dependencies
There are a few dependencies not available in the Chocolatey package database. In order to ease the manual installation process, we provide the necessary Chocolatey packages.
As some chocolatey packages rely on it, we start by installing CMake
choco install -y cmake
You will need to append the CMake bin folder C:\Program Files\CMake\bin to your PATH.
Please download these packages from this GitHub repository.
asio.1.12.1.nupkgbullet.3.17.nupkgcunit.2.1.3.nupkgeigen.3.3.4.nupkgtinyxml-usestl.2.6.2.nupkgtinyxml2.6.0.0.nupkg
Once these packages are downloaded, open an administrative shell and execute the following command:
choco install -y -s <PATH\TO\DOWNLOADS\> asio cunit eigen tinyxml-usestl tinyxml2 bullet
Please replace <PATH\TO\DOWNLOADS> with the folder you downloaded the packages to.
First upgrade pip and setuptools:
python -m pip install -U pip setuptools==59.6.0
Now install some additional python dependencies:
python -m pip install -U catkin_pkg cryptography empy==3.3.4 importlib-metadata lark==1.1.1 lxml matplotlib netifaces numpy opencv-python PyQt5 pillow psutil pycairo pydot pyparsing==2.4.7 pyyaml rosdistro
Install Qt5
Download the 5.12.X offline installer from Qt’s website.
Run the installer.
Make sure to select the MSVC 2017 64-bit component under the Qt -> Qt 5.12.12 tree.
Finally, in an administrator cmd.exe window set these environment variables.
The commands below assume you installed it to the default location of C:\Qt.
setx /m Qt5_DIR C:\Qt\Qt5.12.12\5.12.12\msvc2017_64
setx /m QT_QPA_PLATFORM_PLUGIN_PATH C:\Qt\Qt5.12.12\5.12.12\msvc2017_64\plugins\platforms
Note
This path might change based on the installed MSVC version, the directory Qt was installed to, and the version of Qt installed.
RQt dependencies
To run rqt_graph you need to download and install Graphviz. The installer will ask if to add graphviz to PATH, choose to either add it to the current user or all users.
Downloading ROS 2
Go to the releases page: https://github.com/ros2/ros2/releases
Download the latest package for Windows, e.g.,
ros2-humble-*-windows-release-amd64.zip.
Note
There may be more than one binary download option which might cause the file name to differ.
Note
To install debug libraries for ROS 2, see Extra Stuff for Debug.
Then continue on with downloading ros2-package-windows-debug-AMD64.zip.
Unpack the zip file somewhere (we’ll assume
C:\dev\ros2_humble).
Install additional DDS implementations (optional)
If you would like to use another DDS or RTPS vendor besides the default, Fast DDS, you can find instructions here.
Environment setup
Start a command shell and source the ROS 2 setup file to set up the workspace:
call C:\dev\ros2_humble\local_setup.bat
It is normal that the previous command, if nothing else went wrong, outputs The system cannot find the path specified. exactly once.
Try some examples
In a command shell, set up the ROS 2 environment as described above and then run a C++ talker:
ros2 run demo_nodes_cpp talker
Start another command shell and run a Python listener:
ros2 run demo_nodes_py listener
You should see the talker saying that it’s Publishing messages and the listener saying I heard those messages.
This verifies both the C++ and Python APIs are working properly.
Hooray!
Next steps after installing
Continue with the tutorials and demos to configure your environment, create your own workspace and packages, and learn ROS 2 core concepts.
Additional RMW implementations (optional)
The default middleware that ROS 2 uses is Fast DDS, but the middleware (RMW) can be replaced at runtime.
See the guide on how to work with multiple RMWs.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting techniques can be found here.
Uninstall
If you installed your workspace with colcon as instructed above, “uninstalling” could be just a matter of opening a new terminal and not sourcing the workspace’s
setupfile. This way, your environment will behave as though there is no Humble install on your system.If you’re also trying to free up space, you can delete the entire workspace directory with:
rmdir /s /q \ros2_humble
Extra Stuff for Debug
To download the ROS 2 debug libraries you’ll need to download ros2-humble-*-windows-debug-AMD64.zip.
Please note that debug libraries require some more additional configuration/setup to work as given below.
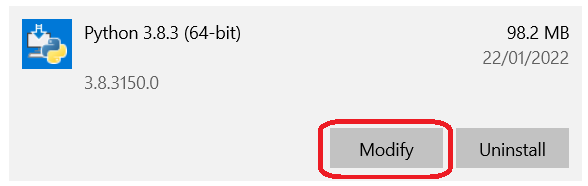
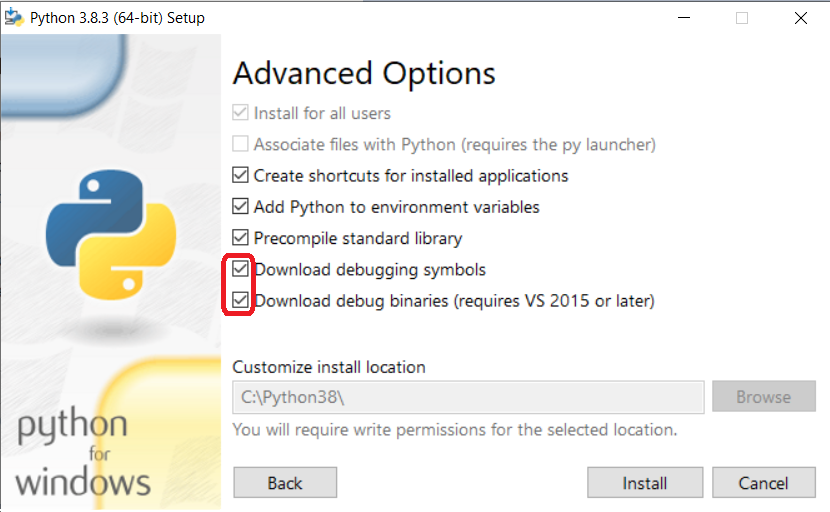
Python installation may require modification to enable debugging symbols and debug binaries:
Search in windows Search Bar and open Apps and Features.
Search for the installed Python version.
Click Modify.
Click Next to go to Advanced Options.
Make sure Download debugging symbols and Download debug binaries are checked.
Click Install.